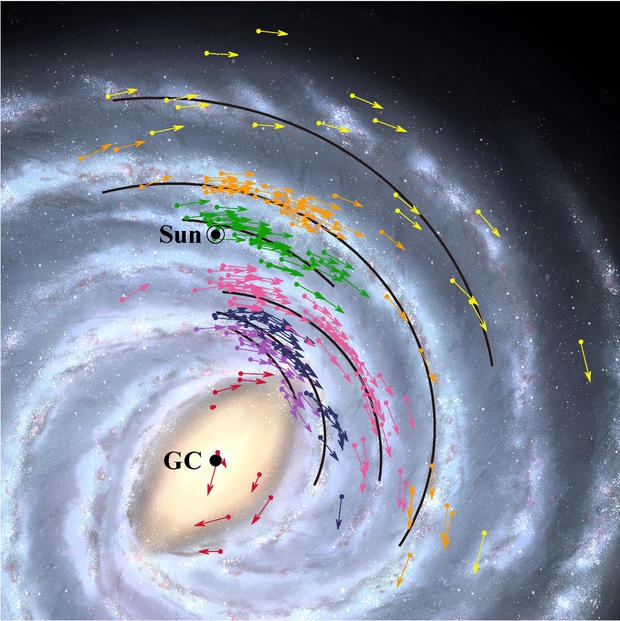
New map of the Milky Way created National Astronomical Laboratory of Japan Shows that the Earth rotates faster and is 2,000 light-years closer to the miraculous black hole at the center of our galaxy than previously thought.
In 1985, the International Astronomical Union announced that the Earth was 27,700 light-years away from a black hole named Sagittarius A *. But a 15-year analysis by the Japanese radio astronomical program VERA found that the Earth is actually only 25,800 light-years away. They also found that the earth was moving at 7 km / s faster than they had previously believed.
Sagittarius A * and black holes like this are called “supermassive” for a reason – they are Billion times more Than the sun.
But the NAOJ said there was no need to worry because recent reports did not indicate the planet was “moving towards the black hole”. This means it is now the “best model of the Milky Way galaxy”.
NAOJ
Using the VERA Astrometry chart, the scientists created a position and velocity map that sets the center of the Milky Way galaxy and the objects that live within it. The first VERA astrometry list was released this year and includes data for 99 objects.
Stabilization indicates that the center of the galaxy where the black hole is located is orbiting the Earth at a speed of 227 km / h. Astronomers initially thought the orbit was 220 km / h.
“Because the Earth’s Milky Way is located inside the galaxy, we can not retreat and see what the galaxy looks like from outside,” NAOJ said in a statement. “Astronomy, the accurate measurement of the positions and motions of objects, is an important tool for understanding the overall structure of the galaxy and our place in it.”
Radio Astrometry’s Vera, Very Long Baseline Interferometry Exploration was developed in 2000 and uses interferometry to integrate data from radio telescopes located throughout Japan. With this project, scientists could develop the same resolution as the 2,300 km diameter telescope, which is “sharp enough in theory to solve an American penny placed on the surface of the moon,” NAOJ said.
NAOJ scientists hope to gather more material data by focusing on those close to Sagittarius A *.

“Food expert. Unapologetic bacon maven. Beer enthusiast. Pop cultureaholic. General travel scholar. Total internet buff.”
 DodoFinance Breaking News Made For You!
DodoFinance Breaking News Made For You!